1. Definition of E-Commerce
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services using the internet. It involves online transactions through websites, mobile apps, and digital platforms. This modern form of trade has revolutionized business operations by making shopping faster, easier, and more accessible to consumers worldwide.

2. Historical Background
The concept of e-commerce began in the early 1990s with the rise of the internet. Companies like Amazon and eBay pioneered online retailing, offering customers the ability to shop from home. Over the decades, e-commerce evolved from simple websites to advanced mobile applications and social media marketplaces, making online shopping a part of everyday life.
3. Types of E-Commerce Models
E-commerce operates through various models:
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Involves transactions between businesses, such as wholesalers selling to retailers.
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): The most common model, where businesses sell directly to individual customers, such as Amazon.
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Platforms like eBay and OLX allow individuals to sell directly to others.
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Freelancers or content creators offering services to companies.
- B2G (Business-to-Government): Businesses providing goods or services to government organizations.
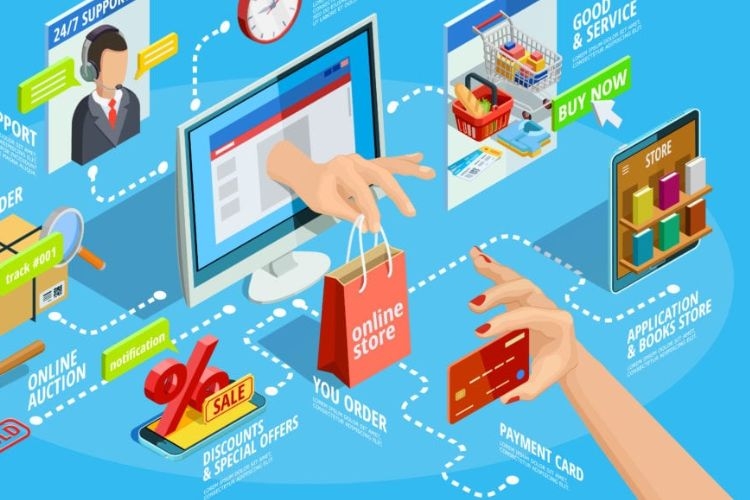

4. Components of E-Commerce
Successful e-commerce systems rely on several key components:
- Website or App Platform: The digital storefront that allows users to browse and purchase.
- Payment Gateways: Secure systems for processing online payments.
- Logistics and Delivery: Managing order fulfillment and shipping.
- Customer Service: Offering support through chatbots or live agents.
- Digital Marketing: Using social media, search engines, and online ads to reach customers.
5. E-Commerce Platforms and Examples
Popular e-commerce platforms include Amazon, Alibaba, eBay, and Shopify, which serve millions of global users. In South Asia, platforms like Daraz are rapidly expanding, while Noon leads in the Middle East. Each platform offers a different approach—some focus on retail, others on wholesale or niche markets.

6. Importance in the Modern Economy
E-commerce has become a cornerstone of today’s digital economy. It supports international trade, creates job opportunities, and enables small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to compete globally. During the COVID-19 pandemic, e-commerce proved essential in keeping businesses running and connecting consumers with essential goods.

7. Advantages for Businesses
Businesses benefit from e-commerce through reduced operating costs, broader market access, and real-time data analytics. Online stores operate 24/7, enabling companies to serve customers globally without physical limitations. Data-driven insights help businesses understand customer behavior, improve marketing strategies, and manage inventory efficiently.

8. Advantages for Consumers
For consumers, e-commerce offers convenience, variety, and time savings. Shoppers can compare prices, read reviews, and make purchases from the comfort of their homes. The availability of global brands, secure payments, and fast delivery options make online shopping increasingly popular.
9. Challenges and Limitations
Despite its growth, e-commerce faces challenges such as cybersecurity threats, online fraud, and data privacy concerns. Delivery delays and issues with product quality can affect customer trust. Moreover, in developing regions, poor internet access and payment barriers limit e-commerce adoption.

10. Technology Used in E-Commerce
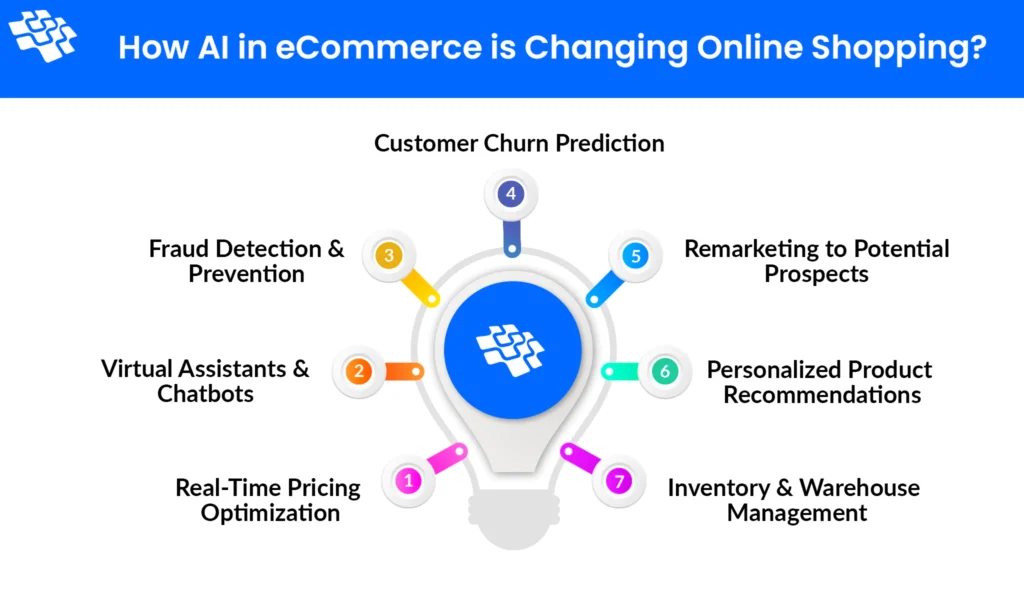
Modern e-commerce relies heavily on technology. Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps personalize shopping experiences and recommend products. Blockchain ensures secure transactions, while cloud computing supports scalability. Big data analytics helps companies predict consumer trends and improve marketing strategies.
11. Digital Payment Systems
A secure and efficient payment system is crucial for e-commerce. Customers can pay using credit or debit cards, digital wallets, mobile banking apps, or even cryptocurrency in some markets. In developing countries, cash on delivery (COD) remains popular due to limited access to online banking.

12. Marketing Strategies in E-Commerce
Digital marketing drives e-commerce success. Businesses use SEO to improve search visibility, social media marketing to engage audiences, and email campaigns to retain customers. Influencer and affiliate marketing also help build trust and attract targeted buyers.

13. E-Commerce in Developing Countries
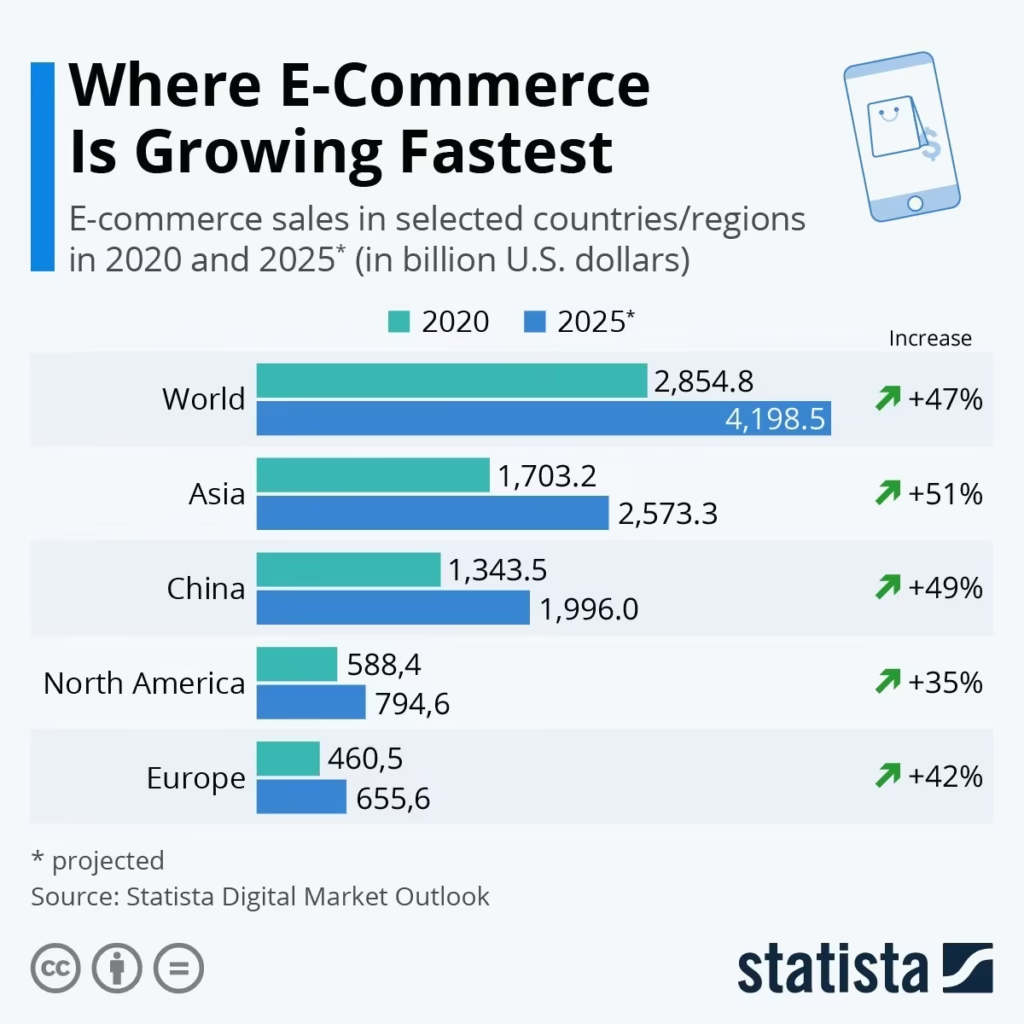
E-commerce is expanding rapidly in developing countries due to increased internet and smartphone usage. It empowers small businesses by giving them access to online marketplaces. However, these regions still face challenges such as unreliable logistics, lack of trust, and limited digital payment systems.
14. Future Trends in E-Commerce
The future of e-commerce looks promising with advancements like mobile commerce (m-commerce), virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR), and AI-driven personalization. Sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly packaging and green logistics, are also shaping consumer preferences.

15. Conclusion
E-commerce has reshaped how people buy, sell, and connect globally. It offers endless opportunities for innovation and growth, but also demands strong cybersecurity and customer trust. As technology continues to advance, e-commerce will remain a vital force in shaping the future of global business.